
Email is a big part of our daily lives, but have you ever wondered how safe your messages really are? If you’re sending sensitive information—like passwords, business details, or personal data—you don’t want just anyone snooping around. That’s where email encryption comes in. Encryption is a method of securing data by converting it into an unreadable format that can only be deciphered by authorized parties.
In this guide, we’ll break down what encryption is, why you need it, and how to use it in Gmail and Outlook.
What Is Encryption?
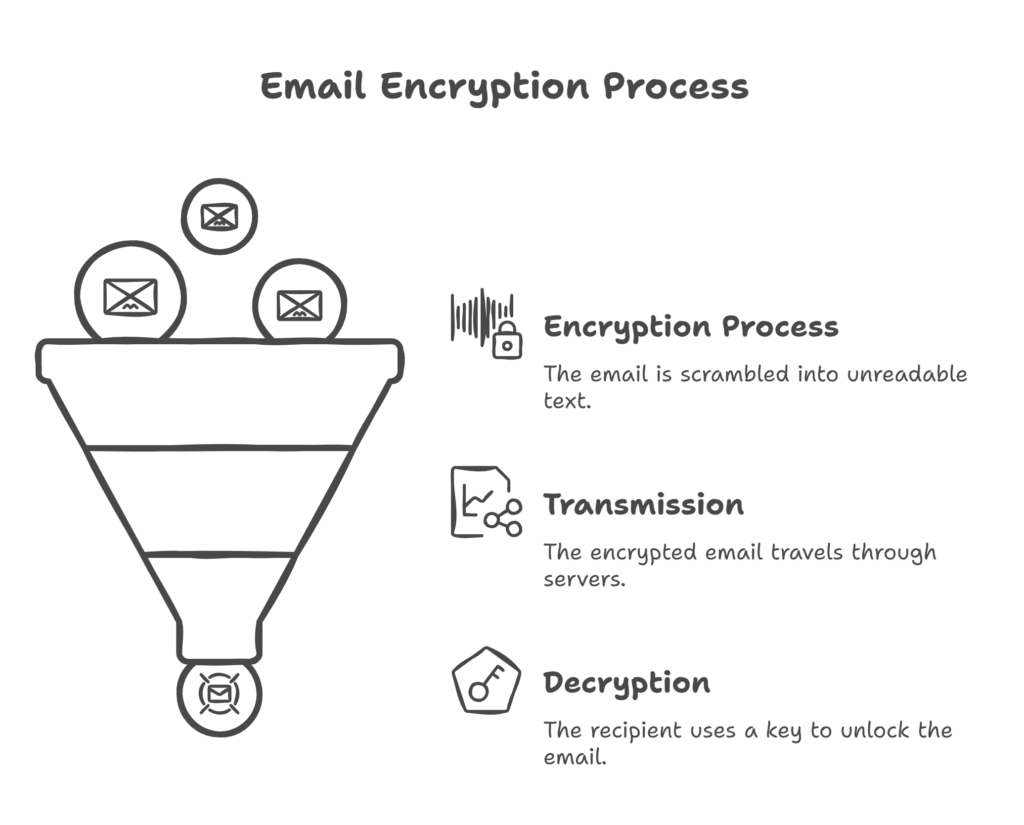
Think of encryption as a secret code. When you send an encrypted email, the message gets scrambled into unreadable text. Only the intended recipient—who has the right “key”—can unlock and read it. In other words, it ensures that sensitive information remains confidential and protected from unauthorized access.
Without encryption, emails travel through multiple servers before reaching the recipient. If someone intercepts them along the way, they might be able to read the content. Encryption helps prevent that.
Why Should You Encrypt Your Emails?
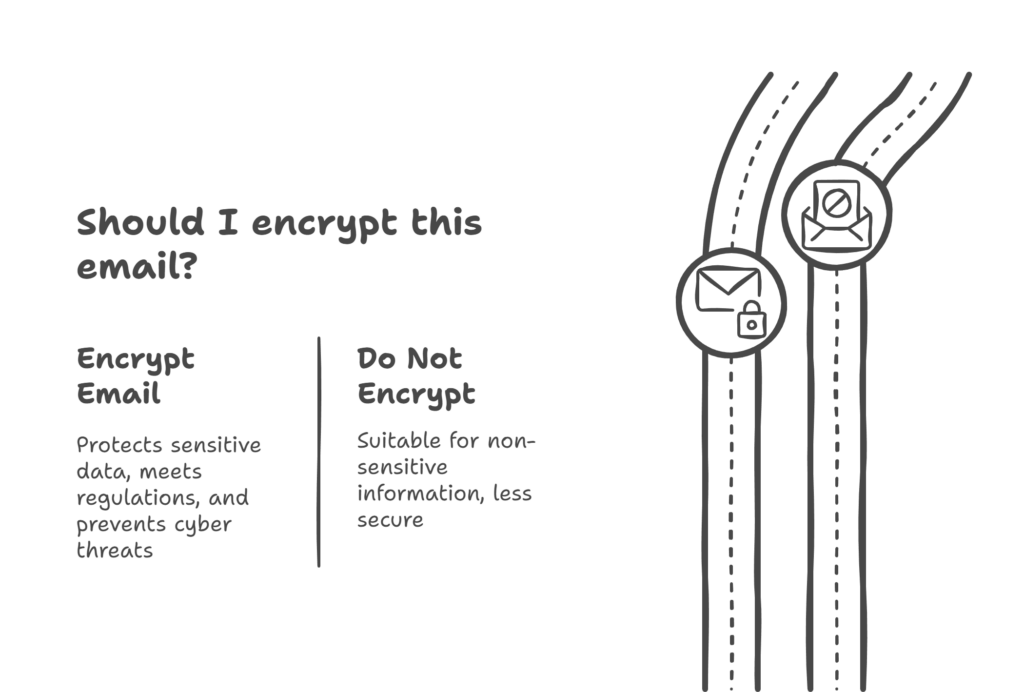
Not all emails need encryption, but in certain cases, it’s important. Here’s why:
🔒 Protect sensitive data – If you send confidential business documents or personal details, encryption keeps them safe.
🏦 Meet security regulations – Industries like healthcare, finance, and law require encrypted emails to protect client information.
👀 Prevent cyber threats – Encryption reduces the risk of hackers intercepting and reading your emails.
If your emails contain anything you wouldn’t want a stranger to see, encryption is a good idea.
Can You Encrypt Emails in Outlook or Gmail?
Yes! Both Gmail and Outlook offer encryption, but the level of encryption depends on the email provider and the type of encryption used.
Outlook supports S/MIME and Microsoft Purview encryption, but you’ll need a Microsoft 365 subscription to use them.
Gmail encrypts messages using TLS by default, but for extra security, you’ll need S/MIME or Client-Side Encryption (CSE)—both of which require a work or school account.
Now, let’s look at how you can encrypt your emails in each platform.
While encryption helps protect sensitive information in emails, another crucial aspect of professional communication is ensuring a consistent and branded email signature. Properly managed email signatures can enhance credibility and maintain company-wide uniformity, especially in business environments where security and professionalism go hand in hand.
How to Encrypt Emails in Outlook
Unlike Gmail, Outlook does NOT enable encryption by default. You need to set up S/MIME or Microsoft Purview encryption manually before you can send encrypted messages. Here is what you need to do start encrypting emails you send from Outlook:
Step 1: Get a Digital Certificate (S/MIME)
Before you can encrypt emails in Outlook, you need a digital ID (certificate). This acts as your “key” to lock and unlock messages.
Obtain a digital certificate from a trusted provider or your IT administrator.
Install the certificate on your computer.
Add the certificate to Outlook by going to Settings > Trust Center > Email Security and selecting Import Digital ID.
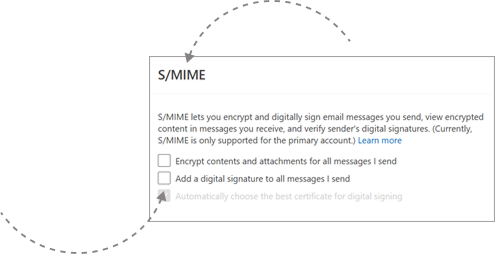
💡 Tip: Outlook does not automatically import certificates, so you must install them manually.
Step 2: Encrypt a Single Email (S/MIME in Outlook)
Once you’ve set up S/MIME, here is how you can encrypt individual emails in Outlook:
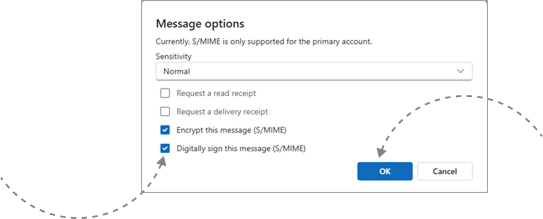
Open a new email.
Click Options > More Options on the ribbon.
Under Message Options, select Encrypt this message (S/MIME).
Finish writing your email and hit Send.
Encrypt All Emails Automatically
Alternatively, you can encrypt all emails that are sent from your address:
Go to Settings > Mail > S/MIME.
Check the box for Encrypt contents for all messages I send.
Click OK to save changes.
Now, all outgoing emails will be encrypted by default!
Encrypt Emails with Microsoft Purview
While composing an email, go to Options > Encrypt.
Choose the level of encryption, such as Encrypt or Do Not Forward.
Finish your email and send it.
📌 Note: This option is available for Microsoft 365 Enterprise users.
How to Encrypt Emails in Gmail
Gmail handles encryption differently than Outlook. Most emails are already encrypted using TLS, but if you need stronger encryption, you have extra options.
Confidential Mode – Extra Privacy Controls
Confidential mode doesn’t encrypt emails, but it adds extra privacy controls by limiting access, restricting forwarding, and setting expiration dates.
How to Send an Email in Confidential Mode:
Open Gmail and click Compose.
At the bottom right of the email window, click the Toggle Confidential Mode button (padlock with a clock icon).
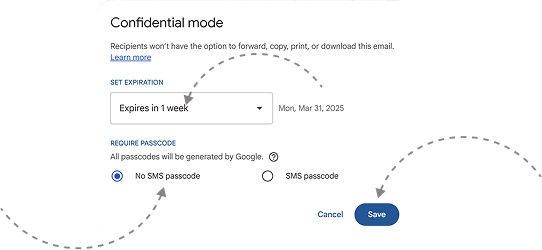
Set an expiration date (e.g., 1 day, 1 week, 1 month, etc.).
Choose whether to require an SMS passcode for extra security.
If you choose “No SMS passcode”, Gmail users can open it directly.
If you choose “SMS passcode”, recipients will receive a text message with a passcode.
Click Save, then send your email.
📌 Note: Recipients can’t copy, download, forward, or print confidential emails.
Standard Encryption (TLS) in Gmail – No Setup Needed
By default, Gmail encrypts emails using Transport Layer Security (TLS). This protects messages while they travel between servers.
💡 Heads up: If the recipient’s email provider doesn’t support TLS, the email won’t be encrypted. Gmail will show a red lock icon ⚠️ to warn you.
Enhanced Encryption (S/MIME) – For Work & School Accounts in Gmail
To use S/MIME in Gmail:
Your IT admin must enable S/MIME for your account.
When composing an email, click the lock icon next to the recipient’s name.
Select Enhanced Encryption (S/MIME).
Send your email.
📌 Both you and the recipient must have S/MIME set up for this to work.
Additional Encryption (Client-Side Encryption - CSE) for Gmail
If your company requires top-level security, Client-Side Encryption (CSE) ensures Google never has access to your encrypted emails.
Your admin must enable CSE for your organization.
When composing an email, click More options > Turn on encryption.
Send your email—only the intended recipient can decrypt it.
💡 Best for: Highly sensitive corporate emails where only your organization manages encryption keys.
Final Thoughts
So, can you encrypt Gmail? Yes, but it depends on your account type. Personal Gmail accounts use TLS encryption by default, while business users can enable S/MIME or Client-Side Encryption (CSE) for stronger protection.
Outlook, on the other hand, does NOT have encryption enabled by default—you’ll need to set up a digital certificate or Microsoft Purview Encryption first.
If you frequently send sensitive emails, it’s worth taking a few minutes to enable encryption. After all, keeping your private information safe is always a smart move!